References
Beeckman D, Campbell J, Campbell K et al (2015) Proceedings of the Global IAD Expert Panel. Incontinence-associated dermatitis: moving prevention forward. Wounds International, London. Available online: www.woundsinternational.com
Beeckman D, Van Damme N, Schoonhoven L, et al (2016) Interventions for preventing and treating incontinence-associated dermatitis in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 11. Art. No.: CD011627. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011627.pub2
Beeckman D (2017) A decade of research on incontinence-associated dermatitis (IAD): Evidence, knowledge gaps and next steps. J Tissue Viability 26(1): 47-56
Beele H, Smet S, Van Damme N, Beeckman D (2018) Incontinence-associated dermatitis: pathogenesis, contributing factors, prevention and management options. Drugs Aging 35: 1-10
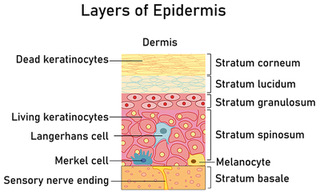
Boer M, Duchnik E, Maleszka R, Marchlewicz M (2016) Structural and biophysical characteristics of human skin in maintaining proper epidermal barrier function. Adv Dermatol Allergol 33(1): 1-5
Collier M, Simon D (2016) Protecting vulnerable skin from moisture-associated skin damage. Br J Nurs 25(20): S26-S32
Dowsett C and Allen L (2013) Moisture-associated skin damage made easy. Wounds UK 9(4): 1-4. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Jones ML (2014) Treating vulnerable skin: the cornerstone of providing good care. Nurs Residential Care 16(12): 671-676
McNichol LL, Ayello EA, Phearman et al (2018) Incontinence-associated dermatitis: state of the science and knowledge. Adv Skin Wound Care 31(11): 502-513
Ousey K and O’Connor L (2017) IAD made easy. Wounds UK 13(1): 1-6. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Penzer R (2012) Best practice in emollient therapy: A statement for healthcare professionals. Dermatol Nurs 11(4): S1-S19
Peters J (2008) Managing eczema at either end of the age spectrum. Dermatol Nurs 7(2): S7-S11
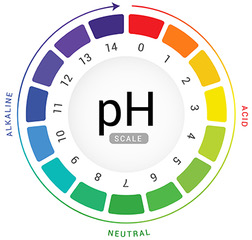
Proksch E (2018) pH in nature, humans and skin. J Dermatol 45: 1044-1052
Rippon M, Colegrave M, Ousey K (2016) Incontinence-associated dermatitis: reducing adverse events. Br J Nurs 25(18): 1016-1021
Schmid-Wendtner MH, Korting HC (2006) The pH of the skin surface and its impact on the barrier fiction. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 19: 296-302
Watkins J (2013) Skin rashes, part 1: Skin structure and taking a dermatological history. Pract Nurs 24(1): 30-33
Wheeler T (2012) Our outermost boundary: the skin. Nurs Residential Care 14(11): 570-576
Wingfield C (2011) Skin care in the older person: a focus on the use of emollients. Br J Community Nurs 16(10): 470-478
Wounds UK (2012) Best Practice Statement: Care of the older person’s skin. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Wounds UK (2018) Best Practice Statement: Maintaining skin integrity. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Young T (2017) Back to basics: understanding Moisture-associated skin damage. Wounds UK 13(2): 56-65
Beeckman D, Van Damme N, Schoonhoven L, et al (2016) Interventions for preventing and treating incontinence-associated dermatitis in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 11. Art. No.: CD011627. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011627.pub2
Beeckman D (2017) A decade of research on incontinence-associated dermatitis (IAD): Evidence, knowledge gaps and next steps. J Tissue Viability 26(1): 47-56
Beele H, Smet S, Van Damme N, Beeckman D (2018) Incontinence-associated dermatitis: pathogenesis, contributing factors, prevention and management options. Drugs Aging 35: 1-10
Boer M, Duchnik E, Maleszka R, Marchlewicz M (2016) Structural and biophysical characteristics of human skin in maintaining proper epidermal barrier function. Adv Dermatol Allergol 33(1): 1-5
Collier M, Simon D (2016) Protecting vulnerable skin from moisture-associated skin damage. Br J Nurs 25(20): S26-S32
Dowsett C and Allen L (2013) Moisture-associated skin damage made easy. Wounds UK 9(4): 1-4. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Jones ML (2014) Treating vulnerable skin: the cornerstone of providing good care. Nurs Residential Care 16(12): 671-676
McNichol LL, Ayello EA, Phearman et al (2018) Incontinence-associated dermatitis: state of the science and knowledge. Adv Skin Wound Care 31(11): 502-513
Ousey K and O’Connor L (2017) IAD made easy. Wounds UK 13(1): 1-6. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Penzer R (2012) Best practice in emollient therapy: A statement for healthcare professionals. Dermatol Nurs 11(4): S1-S19
Peters J (2008) Managing eczema at either end of the age spectrum. Dermatol Nurs 7(2): S7-S11
Proksch E (2018) pH in nature, humans and skin. J Dermatol 45: 1044-1052
Rippon M, Colegrave M, Ousey K (2016) Incontinence-associated dermatitis: reducing adverse events. Br J Nurs 25(18): 1016-1021
Schmid-Wendtner MH, Korting HC (2006) The pH of the skin surface and its impact on the barrier fiction. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 19: 296-302
Watkins J (2013) Skin rashes, part 1: Skin structure and taking a dermatological history. Pract Nurs 24(1): 30-33
Wheeler T (2012) Our outermost boundary: the skin. Nurs Residential Care 14(11): 570-576
Wingfield C (2011) Skin care in the older person: a focus on the use of emollients. Br J Community Nurs 16(10): 470-478
Wounds UK (2012) Best Practice Statement: Care of the older person’s skin. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Wounds UK (2018) Best Practice Statement: Maintaining skin integrity. Available online: www.wounds-uk.com
Young T (2017) Back to basics: understanding Moisture-associated skin damage. Wounds UK 13(2): 56-65


 Success!
Success!